Injection Moulding vs. 3D Printing: A Comprehensive Comparison
In the realm of manufacturing, injection moulding and 3D printing stand out as two predominant methods for producing plastic parts. Each technique offers unique advantages and is suitable for different applications. Here we’ll delve into the intricacies of both processes, comparing their benefits, limitations, and ideal use cases.
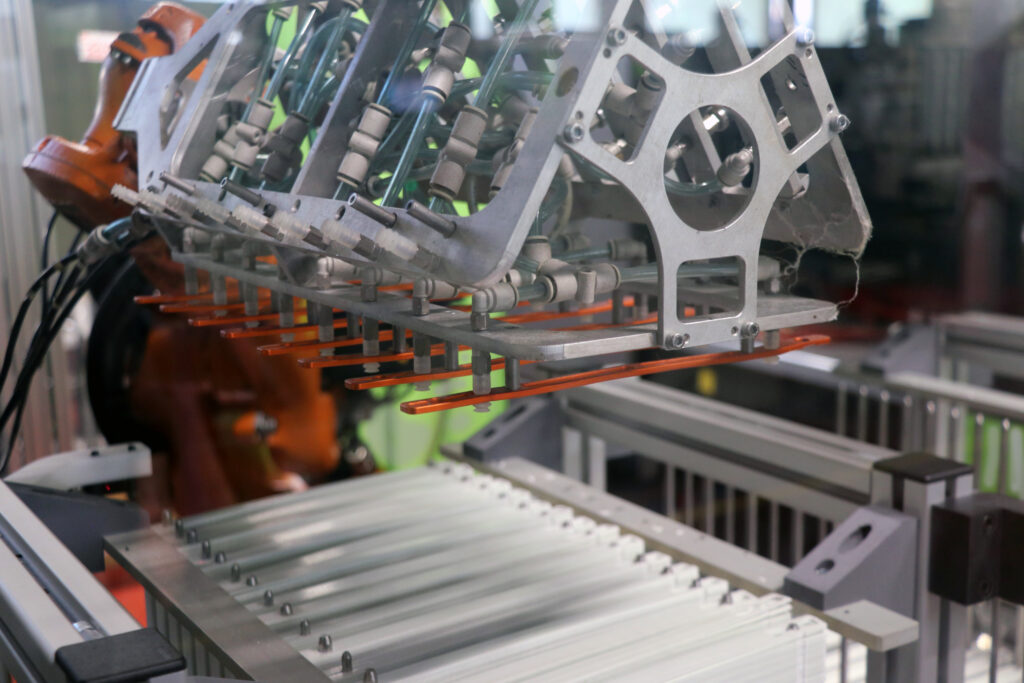
Injection Moulding
Injection moulding is a traditional manufacturing process where molten plastic is injected into a mould cavity. Once the plastic cools and solidifies, it forms the desired part. We at svismold® work efficiently with injection moulding. We have revolutionised the process by integrating fibre tapes into the moulding process.
Advantages of Injection Moulding
- High Efficiency and Productivity: Once the initial setup is complete, injection moulding is capable of producing large volumes of parts at a rapid pace
- Consistency and Precision: This process ensures uniformity and precision, making it ideal for high-quality production runs.
- Material Versatility: A wide range of thermoplastic and thermosetting polymers can be used, allowing for diverse applications.
Limitations of Injection Moulding
- High Initial Costs: The initial investment for mould design and manufacturing is high, which can be a barrier for small-scale production.
- Long Lead Times: The process of designing and manufacturing moulds can take several weeks or even months.
Ideal Applications
Das Spritzgiessen eignet sich am besten für die Serienproduktion, bei der Konsistenz und Präzision entscheidend sind. In Branchen wie die Automobilindustrie, die Medizintechnik oder die Sportbranche findet sich oft diese Methode in der Anwendung.
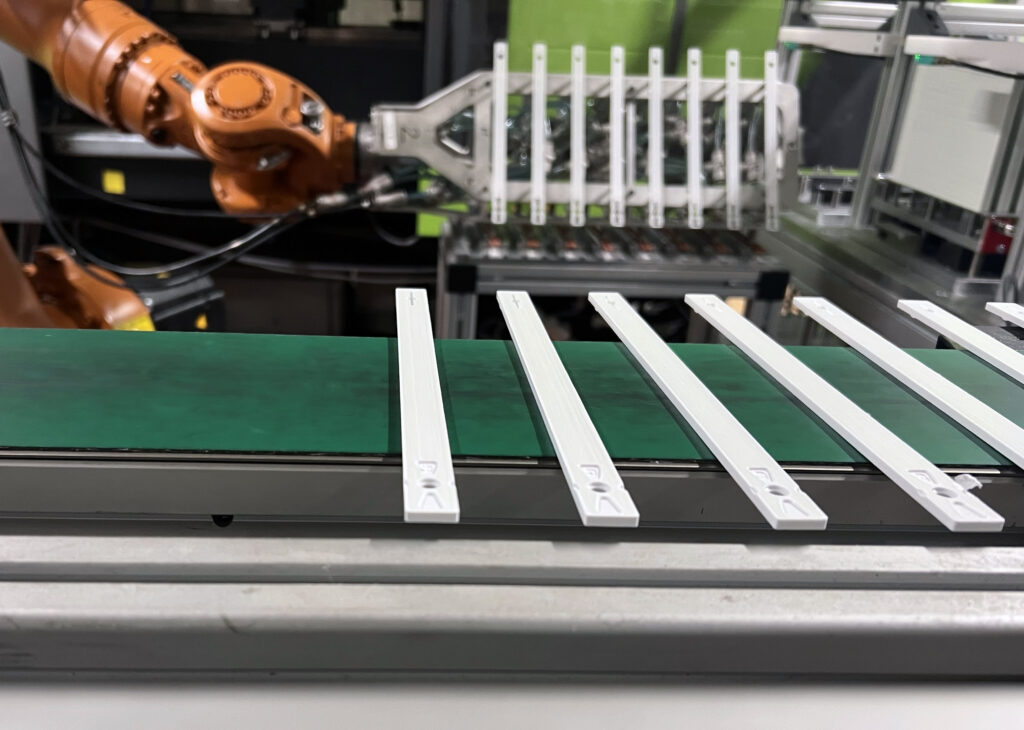

3D Printing
3D printing, or additive manufacturing, creates parts by building layers of material based on a digital model. This process is highly flexible and has revolutionised prototyping and small-scale production. We at svismold® can use 3D printing in our development phase to create fast prototypes.
Advantages of 3D Printing
- Design Flexibility: 3D printing allows for complex geometries and intricate designs that would be difficult or impossible with traditional methods.
- Rapid Prototyping: Designers can quickly produce prototypes, test them, and make adjustments, significantly speeding up the development cycle.
- Low Initial Costs: Since no moulds are required, the initial costs are lower, making it accessible for small runs and custom parts.
- Material Efficiency: Additive manufacturing uses only the material needed for the part, reducing waste.
Limitations of 3D Printing
- Slower Production Speed: 3D printing is generally slower than injection moulding, making it less suitable for high-volume production.
- Limited Material Selection: While material options are expanding, they are still limited compared to injection moulding.
- Surface Finish and Strength: Parts produced by 3D printing often require post-processing to achieve the desired surface finish and may not be as strong as injection moulded parts.
Ideal Applications
3D printing excels in prototyping, custom parts, and small production runs. It is particularly beneficial in industries such as aerospace, healthcare, and creative arts, where custom designs and rapid iterations are essential.
Comparison Summary
Cost Efficiency: Injection moulding is more cost-effective for large volumes, while 3D printing offers lower initial costs for small runs.
Production Speed: Injection moulding is faster for high volumes, whereas 3D printing is ideal for quick prototyping and small batches.
Design Complexity: 3D printing allows for greater design flexibility and complexity, making it suitable for innovative and intricate parts. However, thermoplastic composite parts can also be complex.
Material Selection: Injection moulding offers a broader range of materials, including specialised polymers for various applications.
Precision and Consistency: Injection moulding provides higher precision and consistency, essential for mass production.
Conclusion
Both injection moulding and 3D printing have their unique advantages and are suited for different manufacturing needs. Understanding the strengths and limitations of each method is crucial for selecting the appropriate technology for your project.
svismold® is using 3D printing for prototypes and samples to showcase and test the possibilities. However, for the serial production of high quality thermoplastic parts, svismold® relies on its expertise with injection moulding.
If you are looking for high-volume, consistent production, injection moulding is the way to go. However, for rapid prototyping, custom designs, and small-scale production, 3D printing offers unmatched flexibility and speed.




